标签: pascals-triangle
如何有效地计算pascal三角形中的行?
我有兴趣找到第n行pascal三角形(不是特定元素,而是整行本身).最有效的方法是什么?
我想到了通过总结上面行中相应元素来构造三角形的传统方法:
1 + 2 + .. + n = O(n^2)
另一种方法可能是使用特定元素的组合公式:
c(n, k) = n! / (k!(n-k)!)
对于行中的每个元素,我认为根据计算组合的方式,前一种方法需要更多时间.有任何想法吗?
algorithm combinations binomial-coefficients pascals-triangle
推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数
Code-golf:生成pascal的三角形
生成一个列表列表(或打印,我不介意)一个大小为N 的Pascal三角形,代码可能最少!
这是我的尝试(使用技巧在python 2.6中的 118个字符):
c,z,k=locals,[0],'_[1]'
p=lambda n:[len(c()[k])and map(sum,zip(z+c()[k][-1],c()[k][-1]+z))or[1]for _ in range(n)]
说明:
- 列表理解的第一个元素(当长度为0时)是
[1] - 下一个元素是通过以下方式获得的:
- 取前面的列表并制作两个列表,一个在开头填充0,在结尾填充另一个.
- 例如,对于第二步,我们采取
[1]并制造[0,1]和[1,0]
- 例如,对于第二步,我们采取
- 按元素对两个新列表求和
- 例如,我们制作一个新的列表
[(0,1),(1,0)]并用sum来映射.
- 例如,我们制作一个新的列表
- 重复n次,就是这样.
用法(漂亮的打印,实际上是代码-golf xD):
result = p(10)
lines = [" ".join(map(str, x)) for x in result]
for i in lines:
print i.center(max(map(len, lines)))
输出:
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 …algorithm code-golf combinatorics discrete-mathematics pascals-triangle
推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数
将正常递归转换为尾递归
我想知道是否有一些通用方法来转换"正常"递归foo(...) + foo(...)作为最后一次调用尾递归.
例如(scala):
def pascal(c: Int, r: Int): Int = {
if (c == 0 || c == r) 1
else pascal(c - 1, r - 1) + pascal(c, r - 1)
}
函数式语言的一般解决方案,用于将递归函数转换为尾部调用等效函数:
一种简单的方法是将非尾递归函数包装在Trampolinemonad中.
def pascalM(c: Int, r: Int): Trampoline[Int] = {
if (c == 0 || c == r) Trampoline.done(1)
else for {
a <- Trampoline.suspend(pascal(c - 1, r - 1))
b <- Trampoline.suspend(pascal(c, r - 1))
} yield a + b
} …推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数
Pascal的Python三角形
作为Python的学习经历,我试图编写自己的Pascal三角形版本.它花了我几个小时(因为我刚刚开始),但我出来了这段代码:
pascals_triangle = []
def blank_list_gen(x):
while len(pascals_triangle) < x:
pascals_triangle.append([0])
def pascals_tri_gen(rows):
blank_list_gen(rows)
for element in range(rows):
count = 1
while count < rows - element:
pascals_triangle[count + element].append(0)
count += 1
for row in pascals_triangle:
row.insert(0, 1)
row.append(1)
pascals_triangle.insert(0, [1, 1])
pascals_triangle.insert(0, [1])
pascals_tri_gen(6)
for row in pascals_triangle:
print(row)
返回
[1]
[1, 1]
[1, 0, 1]
[1, 0, 0, 1]
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1]
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1] …推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数
帕斯卡的三角形格式
赋值是在不使用数组的情况下创建Pascal的三角形.我有生成下面三角形值的方法.该方法接受用户想要打印的最大行数的整数.
public static void triangle(int maxRows) {
int r, num;
for (int i = 0; i <= maxRows; i++) {
num = 1;
r = i + 1;
for (int col = 0; col <= i; col++) {
if (col > 0) {
num = num * (r - col) / col;
}
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
我需要格式化三角形的值,使其看起来像一个三角形:
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 …推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数
C++ Pascal的三角形
我正在寻找关于pascal三角形的递归版本如何工作的解释
以下是pascal三角形的递归返回行.
int get_pascal(const int row_no,const int col_no)
{
if (row_no == 0)
{
return 1;
}
else if (row_no == 1)
{
return 1;
}
else if (col_no == 0)
{
return 1;
}
else if (col_no == row_no)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return(get_pascal(row_no-1,col_no-1)+get_pascal(row_no-1,col_no));
}
}
我得到了算法的工作原理我想知道递归是如何工作的.
推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数
帕斯卡的三角形二维数组 - 格式化打印输出
我有一个小任务,我必须使用二维数组来生成帕斯卡三角形。这是我的代码,它有效。如果我像这样显示三角形,还有一个额外的信用机会:
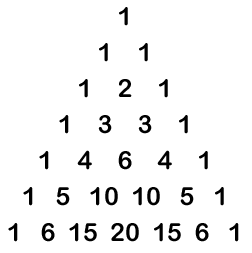
但是,我的间距不是那样格式化的。它只是显示所有排列在左侧的数字。这很难描述,但如果你运行它,你就会明白我的意思。
这是我的代码:
public class Pascal {
public static final int ROW = 16;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] pascal = new int[ROW + 1][];
pascal[1] = new int[1 + 2];
pascal[1][1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= ROW; i++) {
pascal[i] = new int[i + 2];
for (int j = 1; j < pascal[i].length - 1; j++) {
pascal[i][j] = pascal[i - 1][j - 1] + pascal[i - 1][j];
}
}
for (int i …推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数
向一叠玻璃杯中加水
我一直想知道帕斯卡三角形是否有任何实际应用,而不仅仅是二项式展开式的系数。
\n我试图解决这个问题:
\n\n\n但是,如果我添加 K 个单位的水,并且想要找到一个水含量最少的玻璃杯,该怎么办:
\n其中,Glass 将被发现为: 第 -th 行c中的 -th glassr
我相信。如果我们能找到这个,那么我们就不难找到任意玻璃杯中的水量了。{i<r and j<c}
- \n
问题:
\n输入\n添加的水 - K 单位,每个玻璃杯的容量为 1- 单位
\n预期输出:第排
\nc中的第一个玻璃杯r中的水最少。 \n
我试图通过记录每行开始溢出时的容量来解决问题:\n并想知道如何继续使用此方法。
\n 1 max = 1, cap = 1\n 1 1 max = 1, sum(coefficients)=2**1 = 2, cap = 2/1 \n 1 2 1 max = 2, sum = 2**2, cap = 4/2 = …推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数
如何在二维数组中切换行和列?
我正在编写一个代码,它将创建一个可视化的谢尔宾斯基三角形以进行 3D 打印,为了使其工作,我必须使用将创建数组的 Pascal 三角形算法,以便我可以用来告诉我的算法将创建我的三角形不放三角形的地方。
无论如何,问题是,我排列三角形的代码按列而不是像 Pascal 算法那样按行创建三角形,所以我只是想通过重新排列 Pascal 数组的子例程来快速修复。我只是被难住了如何去做,因为我不知道如何避免index out of range错误。
这是为帕斯卡三角形创建数组的代码。
TL:DR我正在尝试重新排列一个数组,其中行是列,列是行
def pascal(n):
"""Prints out n rows of Pascal's triangle."""
row = [1]
global array
array = [[0 for x in range(int(n))] for y in range(int(n))]
array[0]=row
k = [0]
for x in range(int(max(n,0)-1)):
row=[l+r for l,r in zip(row+k,k+row)]
array[x+1]=row
return 1
这是打印数组的输出。我只希望行是列,列是行
def pascal(n):
"""Prints out n rows of Pascal's triangle."""
row = [1]
global array
array = [[0 for x in …python arrays algorithm multidimensional-array pascals-triangle
推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数
帕斯卡三角形与递归
好的,有人可以告诉我,我的当前代码是否可行.我必须使用输入创建pascals三角形而不使用任何循环.我一定会递归.
我花了3天时间,这是我能想到的最好的输出.它驱使我INSANE
def pascal(curlvl,newlvl,tri):
if curlvl == newlvl:
return ""
else:
tri.append(tri[curlvl])
print(tri)
return pascal(curlvl+1,newlvl,tri)
def triLvl():
msg = "Please enter the number of levels to generate:"
triheight = int(input(msg))
if triheight < 1:
print("\n Sorry, the number MUST be positive\n Please try again.")
return triLvl()
else:
return triheight
def main():
triangle = [1]
curlvl = 0
print("Welcome to the Pascal's triangle generator.")
usrTri = triLvl()
print(triangle)
pascal(curlvl,usrTri,triangle)
main()
推荐指数
解决办法
查看次数

