Ulam的螺旋(素数螺旋)
Ale*_*lex 2 c# algorithm primes
我正在寻找想法/代码(最好是C#,但其他语言也可以工作)来创建Ulam的Spiral无限大(受程序运行时间的限制,或直到停止).
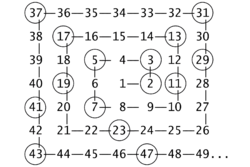
现在这些数字都是素数,因此这些代码相当无关紧要.有趣的是如何在不断增长的(无限)螺旋中编码排列,什么样的数据结构有利于支持它,以及输出的想法(图形文件,文本文件?).
你会怎么做?
考虑每边的长度:1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4 ......
直截了当的是迭代每一面,渲染那一面.您可以使用LOGO样式渲染基元:
Angle = 0;
x=0; y = 0;
int number = 1;
int sideLength = 1;
StartLine();
for (int side = 1; side < maxSize; side++) {
for (int k = 0; k < sideLength; k++) {
Forward(1);
number++;
if (isPrime(number)) {
StopLine();
Ouput(number);
StartLine();
}
}
TurnLeft();
if (side % 2 == 0) sideLength++;
}
你可以通过迭代一边的素数来改善这个:
以下程序通过直接计算数字的坐标来工作.该方法NumberToPoint()执行以下映射.
0 => (x0 , y0 )
1 => (x0 + 1, y0 )
2 => (x0 + 1, y0 - 1)
3 => (x0 , y0 - 1)
4 => (x0 - 1, y0 - 1)
5 => (x0 - 1, y0 )
6 => ...
其余的是一个非常简单的素数测试和一个小型控制台应用程序.
为了保存图像,我会考虑两种解决方案.如果可以为整个图像创建缓冲区,则可以使用下面的程序填充缓冲区.
如果缓冲区很大,我会创建一个方法PointToNumber()并反转计算 - 该方法采用两个坐标并返回此时的数字.使用此方法,您可以从上到下,从左到右迭代并计算此时的数字,检查它是否为素数,并在没有缓冲区的情况下输出像素.但是对于这两种解决方案,在开始之前应该知道图像大小,因为在顶部和左侧添加像素非常昂贵(但是可能).
问题
- 将系数查找转换
NumberToPoint()为坚如磐石的数学而不使用模数,整数除法和签名一千次的任何好主意? - 有什么好的想法可以缩短或加快素数测试?
码
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
namespace UlamsSpiral
{
public static class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Int32 width = 60;
Int32 height = 60;
Console.SetWindowSize(Math.Min(width, 120), Math.Min(height, 60));
Console.SetBufferSize(width, height);
Console.CursorVisible = false;
Int32 limit = (Int32)Math.Pow(Math.Min(width, height) - 2, 2);
for (Int32 n = 1; n <= limit; n++)
{
Point point = NumberToPoint(n - 1, width / 2 - 1, height / 2);
Console.ForegroundColor = n.IsPrime() ? ConsoleColor.DarkBlue : ConsoleColor.DarkGray;
Console.SetCursorPosition(point.X, point.Y);
Console.Write('\u25A0');
Console.SetCursorPosition(0, 0);
Console.Write(n);
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static Point NumberToPoint(Int32 n, Int32 x0, Int32 y0)
{
Int32[,] c = { { -1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0 }, { -1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 1, 0, 1, 1, -1, -1 }, { 1, -1, 0, -1, 0, -1 } };
Int32 square = (Int32)Math.Floor(Math.Sqrt(n / 4));
Int32 index;
Int32 side = (Int32)Math.DivRem(n - 4 * square * square, 2 * square + 1, out index);
Int32 x = c[side, 0] * square + c[side, 1] * index + c[side, 2];
Int32 y = c[side, 3] * square + c[side, 4] * index + c[side, 5];
return new Point(x + x0, y + y0);
}
private static Boolean IsPrime(this Int32 n)
{
if (n < 3) return (n == 2);
return Enumerable.Range(2, (Int32)Math.Sqrt(n)).All(m => n % m != 0);
}
}
}