如何使用 Jetpack Compose 创建 GridView
Gop*_*i S 13 android android-jetpack-compose android-jetpack-compose-list
如何在不使用回收器视图或 android.widget.gridview 的情况下在 Jetpack compose 中创建 Gridview?
Gab*_*tti 24
随着1.0.x该LazyVerticalGrid组合的提供实验支持在网格中显示的项目。
val numbers = (0..20).toList()
LazyVerticalGrid(
cells = GridCells.Fixed(4)
) {
items(numbers.size) {
Column(horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally) {
Text(text = "Number")
Text(text = " $it",)
}
}
}
这 cells = GridCells.Fixed(4)意味着有 4 列是父级宽度的 1/4。
val numbers = (0..20).toList()
LazyVerticalGrid(
cells = GridCells.Adaptive(minSize = 64.dp)
) {
items(numbers) {
Column(horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally) {
Text(text = "Number")
Text(text = " $it",)
}
}
}
cells = GridCells.Adaptive(minSize = 64.dp) 这意味着将有尽可能多的列,每列至少为 64.dp,所有列的宽度相同。
Pav*_*nko 19
UPD:Compose 版本 1.0.0-alpha09 引入了标准组件:
懒惰垂直网格
另一个基于 LazyColumnFor 的解决方案(Jetpack Compose 版本 1.0.0-alpha04)
@Composable
fun <T> LazyGridFor(
items: List<T>,
rowSize: Int = 1,
itemContent: @Composable BoxScope.(T) -> Unit,
) {
val rows = items.chunked(rowSize)
LazyColumnFor(rows) { row ->
Row(Modifier.fillParentMaxWidth()) {
for ((index, item) in row.withIndex()) {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxWidth(1f / (rowSize - index))) {
itemContent(item)
}
}
}
}
}
@Preview("LazyGridFor: example")
@Composable()
fun LazyGridForPreview() {
val data = (1..100).map(Integer::toString)
LazyGridFor(data, 3) { item ->
Text(item)
}
}
我创建了一个自适应网格布局:
预览
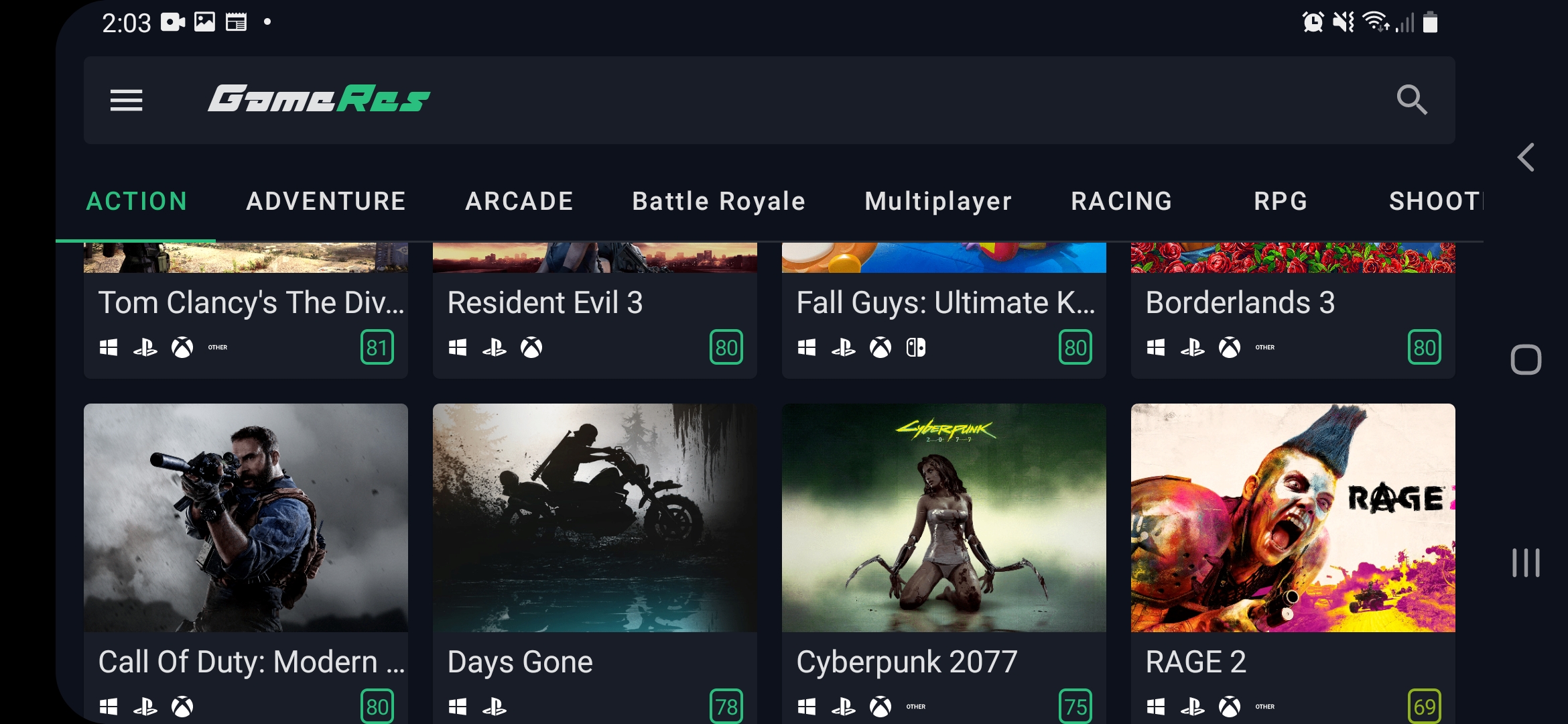

代码
LazyColumn(modifier = modifier) {
...
val numberOfItemsByRow = LocalConfiguration.current.screenWidthDp / 200 // you can replace 200 by the minimum size you want your cells to have.
items(items = trendingGameList.chunked(numberOfItemsByRow)) { rowItems ->
Row(
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(14.dp),
modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 16.dp),
) {
for (game in rowItems) {
GameCard(game = game, onClick = { }, modifier = Modifier.weight(1F))
}
}
Spacer(Modifier.height(14.dp))
}
...
}
完整的代码在这里。
我决定实现我自己的自适应网格布局,因为现有的LazyVerticalGrid是实验性的,将来可以删除,并且要使用它,您必须以@ExperimentalFoundationApi递归方式注释使用它的可堆肥:
@ExperimentalFoundationApi
@Composable
fun A {
LazyVerticalGrid {
...
}
}
@ExperimentalFoundationApi
@Composable
fun B {
A {..}
}
@ExperimentalFoundationApi
@Composable
fun C {
B {..}
}
...
或者使用@OptIn(ExperimentalFoundationApi::class)需要-Xopt-in=kotlin.RequiresOptIn编译器参数的。
正如@Pavel Marchenko 提到的,LazyVerticalGrid是从版本中添加的1.0.0-alpha09
这是一个快速示例:
LazyVerticalGrid(
cells = GridCells.Adaptive(96.dp),
contentPadding = PaddingValues(16.dp),
) {
items(bookList) { book ->
Image(book.cover, modifier = Modifier.padding(8.dp))
}
}
小智 6
更新 @Pavel Marchenko 答案,因为一些 compose 函数的名称发生了更改:LazyColumn() 而不是 LazyColumnFor() 并且需要使用 items() 函数:
@Composable
fun <T> LazyGridFor(
items: List<T>,
rowSize: Int = 1,
itemContent: @Composable BoxScope.(T) -> Unit,
) {
LazyColumn {
items(items = items.chunked(rowSize)) { row ->
Row(Modifier.fillParentMaxWidth()) {
for ((index, item) in row.withIndex()) {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxWidth(1f / (rowSize - index))) {
itemContent(item)
}
}
}
}
}
}
| 归档时间: |
|
| 查看次数: |
6627 次 |
| 最近记录: |

