如何迭代二叉树?
unj*_*nj2 10 java algorithm recursion binary-tree traversal
现在我有
private static void iterateall(BinaryTree foo) {
if(foo!= null){
System.out.println(foo.node);
iterateall(foo.left);
iterateall(foo.right);
}
}
你能把它改成Iteration而不是递归吗?
pol*_*nts 42
您正在寻找的是后继算法.
以下是它的定义方式:
- 第一条规则:树中的第一个节点是树中最左边的节点.
- 下一个规则:节点的后继者是:
- Next-R规则:如果它有一个右子树,则右子树中最左边的节点.
- Next-U规则:否则,遍历树
- 如果右转(即此节点是左子节点),则该父节点是后继节点
- 如果你左转(即这个节点是一个正确的孩子),继续上升.
- 如果你再也不能上去了,那就没有继任者了
如您所见,为此,您需要一个父节点指针.
例:
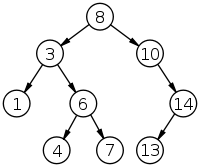
- 第一条规则:树中的第一个节点是树中最左边的节点:
(1) - Next-U规则:由于
(1)没有正确的子树,我们去了(3).这是右转,(3)下一步也是如此. - Next-R规则:由于
(3)有一个正确的子树,该子树中最左边的节点是下一个:(4). - Next-U规则:由于
(4)没有正确的子树,我们去了(6).这是右转,接下来就是(6). - Next-R规则:由于
(6)有一个正确的子树,该子树中最左边的节点是下一个:(7). - Next-U规则:由于
(7)没有正确的子树,我们去了(6).这是一个左转,所以我们继续前进(3).这是一个左转,所以我们继续前进(8).这是右转,接下来就是(8). - Next-R规则:由于
(8)有一个正确的子树,该子树中最左边的节点是下一个:(10). - Next-R规则:由于
(10)有一个正确的子树,该子树中最左边的节点是下一个:(13). - Next-U规则:由于
(13)没有正确的子树,我们去了(14).这是右转,接下来就是(14). - Next-U规则:由于
(14)没有正确的子树,我们去了(10).这是一个左转,所以我们继续前进(8).这是一个左转,所以我们想继续上升,但由于(8)没有父母,我们已经到了最后.(14)没有接班人.
伪代码
Node getLeftMost(Node n)
WHILE (n.leftChild != NULL)
n = n.leftChild
RETURN n
Node getFirst(Tree t)
IF (t.root == NULL) RETURN NULL
ELSE
RETURN getLeftMost(t.root);
Node getNext(Node n)
IF (n.rightChild != NULL)
RETURN getLeftMost(n.rightChild)
ELSE
WHILE (n.parent != NULL AND n == n.parent.rightChild)
n = n.parent;
RETURN n.parent;
PROCEDURE iterateOver(Tree t)
Node n = getFirst(t);
WHILE n != NULL
visit(n)
n = getNext(n)
Java代码
这是上述算法的简单实现:
public class SuccessorIteration {
static class Node {
final Node left;
final Node right;
final int key;
Node parent;
Node(int key, Node left, Node right) {
this.key = key;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
if (left != null) left.parent = this;
if (right != null) right.parent = this;
}
Node getLeftMost() {
Node n = this;
while (n.left != null) {
n = n.left;
}
return n;
}
Node getNext() {
if (right != null) {
return right.getLeftMost();
} else {
Node n = this;
while (n.parent != null && n == n.parent.right) {
n = n.parent;
}
return n.parent;
}
}
}
}
然后你就可以拥有这样的测试工具:
static Node C(int key, Node left, Node right) {
return new Node(key, left, right);
}
static Node X(int key) { return C(key, null, null); }
static Node L(int key, Node left) { return C(key, left, null); }
static Node R(int key, Node right) { return C(key, null, right); }
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node n =
C(8,
C(3,
X(1),
C(6,
X(4),
X(7)
)
),
R(10,
L(14,
X(13)
)
)
);
Node current = n.getLeftMost();
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.key + " ");
current = current.getNext();
}
}
这打印:
1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
也可以看看
你能把它改成Iteration而不是递归吗?
您可以使用显式堆栈.伪代码:
private static void iterateall(BinaryTree foo) {
Stack<BinaryTree> nodes = new Stack<BinaryTree>();
nodes.push(foo);
while (!nodes.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTree node = nodes.pop();
if (node == null)
continue;
System.out.println(node.node);
nodes.push(node.right);
nodes.push(node.left);
}
}
但这并不比递归代码优越(除了代码中缺少的基本条件).
- "不优越":我同意.虽然很高兴知道所有递归算法都可以转换为迭代算法以及如何完成,但如果实际完成它通常不会带来任何显着优势. (3认同)
- @specializt 基本上你所说的每件事都是错误的。您似乎将用迭代替换递归等同于用更复杂的算法替换简单的算法。这是“有时”很自然的事情(计算斐波那契数是典型的例子),但这不是必然的结果。迭代算法可能(内存/时间)效率低下。相反,递归可以是高效的。例如,斐波那契数的自然递归计算可以与规范迭代版本一样高效(使用 O(1) 空间,在 O(n) 时间内运行)。 (3认同)