参考:mod_rewrite,URL重写和"漂亮的链接"解释
dec*_*eze 138 apache .htaccess mod-rewrite friendly-url
"漂亮的链接"是一个经常被要求的主题,但它很少被完全解释.mod_rewrite是制作"漂亮链接"的一种方法,但它很复杂,其语法非常简洁,难以理解,文档假定HTTP具有一定程度的熟练程度.有人可以用简单的术语解释"漂亮的链接"是如何工作的以及如何使用mod_rewrite来创建它们?
其他常见名称,别名,干净网址术语:RESTful URL,用户友好的URL,SEO友好的URL,Slugging,MVC url(可能用词不当)
dec*_*eze 104
要了解什么mod_rewrite,您首先需要了解Web服务器的工作原理.Web服务器响应HTTP请求.最基本级别的HTTP请求如下所示:
GET /foo/bar.html HTTP/1.1
这是浏览器向Web服务器请求URL 的简单请求/foo/bar.html.重要的是要强调它不请求文件,它只请求一些任意URL.请求也可能如下所示:
GET /foo/bar?baz=42 HTTP/1.1
这与URL的请求一样有效,而且它显然与文件无关.
Web服务器是一个侦听端口的应用程序,接受来自该端口的HTTP请求并返回响应.Web服务器完全可以以任何方式响应任何请求,以任何方式对其进行响应.此响应不是文件,它是HTTP响应,可能与任何磁盘上的物理文件有任何关系.Web服务器不一定是Apache,还有许多其他Web服务器,它们都只是持久运行并附加到响应HTTP请求的端口的程序.你可以自己写一个.本段旨在使您与URL直接等于文件的任何概念脱节,这对于理解非常重要.:)
大多数Web服务器的默认配置是查找与硬盘上的URL匹配的文件.如果服务器的文档根目录设置为,/var/www则可以查看该文件是否/var/www/foo/bar.html存在并提供服务(如果存在).如果文件以".php"结尾,它将调用PHP解释器,然后返回结果.所有这些关联都是完全可配置的; 一个文件不必以".php"结尾,以便Web服务器通过PHP解释器运行它,并且URL不必与磁盘上的任何特定文件匹配.
mod_rewrite是一种重写内部请求处理的方法.当Web服务器收到URL请求时/foo/bar,您可以在Web服务器在磁盘上查找与之匹配的文件之前将该URL 重写为其他内容.简单的例子:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteRule /foo/bar /foo/baz
此规则表示每当请求与"/ foo/bar"匹配时,将其重写为"/ foo/baz".然后将处理该请求,就好像/foo/baz已经请求了一样.这可用于各种效果,例如:
RewriteRule (.*) $1.html
此规则匹配任何(.*)并捕获它((..)),然后重写它以附加".html".换句话说,如果/foo/bar是请求的URL,它将被处理,就像/foo/bar.html被请求一样.有关正则表达式匹配,捕获和替换的更多信息,请参见http://regular-expressions.info.
另一个经常遇到的规则是:
RewriteRule (.*) index.php?url=$1
这再次匹配任何内容并将其重写到文件index.php,并在url查询参数中附加最初请求的URL .即,对于任何和所有请求进入,文件index.php被执行,并且该文件将有权访问原始请求$_GET['url'],因此它可以用它做任何想做的事情.
主要是将这些重写规则放入Web服务器配置文件中.Apache还允许您将它们放入.htaccess文档根目录中调用的文件中(即.php文件旁边).
*如果主Apache配置文件允许; 它是可选的,但通常是启用的.
mod_rewrite 没有做什么
mod_rewrite并没有神奇地使你的所有网址"漂亮".这是一种常见的误解.如果您的网站中有此链接:
<a href="/my/ugly/link.php?is=not&very=pretty">
mod_rewrite没有什么可以做的那么漂亮.为了使它成为一个漂亮的链接,你必须:
将链接更改为漂亮的链接:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)<a href="/my/pretty/link">使用服务器上的mod_rewrite
/my/pretty/link使用上述任何一种方法处理对URL的请求.
(可以mod_substitute结合使用来转换传出的HTML页面及其包含的链接.虽然这比仅仅更新HTML资源更有用.)
有很多mod_rewrite可以做,你可以创建非常复杂的匹配规则,包括链接几个重写,将请求代理到完全不同的服务或机器,返回特定的HTTP状态代码作为响应,重定向请求等.它非常强大,可以用来如果您了解基本的HTTP请求 - 响应机制,那将非常有用.它并不会自动让你的链接漂亮.
有关所有可能的标志和选项,请参阅官方文档.
- 也许提及版本2.2.16中引入的[FallbackResource指令](https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/rewrite/remapping.html#fallback-resource)作为[preffered way](https:// httpd)重写给调度员的.apache.org/docs/2.4/rewrite/remapping.html#fallback-resource. (6认同)
Nic*_*ick 76
为了扩展deceze的答案,我想提供一些示例和一些其他mod_rewrite功能的解释.
以下所有示例均假定您已包含RewriteEngine On在您的.htaccess文件中.
重写示例
让我们举个例子:
RewriteRule ^blog/([0-9]+)/([A-Za-z0-9-\+]+)/?$ /blog/index.php?id=$1&title=$2 [NC,L,QSA]
该规则分为4个部分:
RewriteRule- 启动重写规则^blog/([0-9]+)/([A-Za-z0-9-\+]+)/?$- 这被称为模式,但是我只是将它称为规则的左侧 - 你要重写的是什么blog/index.php?id=$1&title=$2- 称为重写规则的替换或右侧 - 您要重写的内容[NC,L,QSA]是重写规则的标志,用逗号分隔,我稍后会详细解释
上面的重写将允许您链接到类似的东西/blog/1/foo/,它实际上会加载/blog/index.php?id=1&title=foo.
规则的左手边
^表示页面名称的开头 - 因此它将重写example.com/blog/...但不会重写example.com/foo/blog/...- 每组
(…)括号表示一个正则表达式,我们可以将其捕获为规则右侧的变量.在这个例子中: ?意味着,前面的字符是可选的,因此在这两个这种情况下/blog/1/foo/并且/blog/1/foo将重写到同一个地方$表示这是我们想要匹配的字符串的结尾
旗
这些是在重写规则末尾的方括号中添加的选项,用于指定特定条件.同样,你可以在文档中阅读很多不同的标志,但我将介绍一些更常见的标志:
NC
无案例标志意味着重写规则不区分大小写,因此对于上面的示例规则,这意味着将匹配两者/blog/1/foo/和/BLOG/1/foo/(或其任何变体).
L
最后一个标志表示这是应该处理的最后一条规则.这意味着当且仅当此规则匹配时,才会在当前重写处理运行中评估其他规则.如果规则不匹配,则将照常按顺序尝试所有其他规则.如果未设置该L标志,则之后将对所有以下规则应用于重写的 URL.
END
从Apache 2.4开始,您也可以使用该[END]标志.与它匹配的规则将完全终止进一步的别名/重写处理.(而[L]标志通常可以触发第二轮,例如重写到子目录或从子目录重写时.)
QSA
查询字符串append标志允许我们将额外的变量传递给指定的URL,该URL将被添加到原始的get参数中.对于我们的例子,这意味着/blog/1/foo/?comments=15会加载/blog/index.php?id=1&title=foo&comments=15
R
这个标志不是我在上面的例子中使用的标志,但是我认为值得一提.这允许您指定http重定向,并带有包含状态代码的选项(例如R=301).例如,如果您想在/ myblog/to/blog /上执行301重定向,您只需编写如下规则:
RewriteRule ^/myblog/(*.)$ /blog/$1 [R=301,QSA,L]
重写条件
重写条件使重写更加强大,允许您为更具体的情况指定重写.您可以在文档中了解很多条件,但我会介绍几个常见示例并解释它们:
# if the host doesn't start with www. then add it and redirect
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^www\.
RewriteRule ^ http://www.%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
这是一种非常常见的做法,它会在您的域前加上www.(如果它不存在)并执行301重定向.例如,加载http://example.com/blog/它会将您重定向到http://www.example.com/blog/
# if it cant find the image, try find the image on another domain
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} \.(jpg|jpeg|gif|png)$ [NC]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule (.*)$ http://www.example.com/$1 [L]
这稍微不那么常见,但如果文件名是服务器上存在的目录或文件,则这是一个不执行的规则的好例子.
%{REQUEST_URI} \.(jpg|jpeg|gif|png)$ [NC]只会对文件扩展名为jpg,jpeg,gif或png(不区分大小写)的文件执行重写.%{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f将检查当前服务器上是否存在该文件,如果不存在则仅执行重写%{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d将检查当前服务器上是否存在该文件,如果不存在则仅执行重写- 重写将尝试在另一个域上加载相同的文件
mar*_*rio 36
参考
Stack Overflow还有许多其他很好的资源可供使用:
- Serverfault:你想知道的关于mod_rewrite的所有内容
(请记住删除^/模式前缀中的斜杠以供.htaccess使用.) - 在mod_rewrite的隐藏功能中做和不做.
- 查看我们最受欢迎的mod-rewrite问题和答案.
- Apache 重定向和重新映射指南.
- AskApache 终极.htaccess指南
- 而国防部重写 标签维基引用.
对新人友好的正则表达式概述甚至:
- 我们的正则表达式 标记维基用于语法概要.
- 而简短的Apache正则表达式总结.
- 其他regexp.info用于易于理解的基础知识.
Oft-used占位符
.*匹配任何东西,甚至是空字符串.您不希望在任何地方使用此模式,但通常在最后一个回退规则中使用.[^/]+更常用于路径段.除了正斜杠之外,它匹配任何东西.\d+只匹配数字字符串.\w+匹配字母数字字符.它基本上是简写[A-Za-z0-9_].[\w\-]+对于"slug"式的路径段,使用字母,数字,短划线-和_[\w\-.,]+添加句号和逗号.首选\-在[…]charclasses中的转义破折号.\.表示文字期间.否则,.外面的[…]为任何符号的占位符.
这些占位符中的每一个通常都用(…)括号括起来作为捕获组.整个模式通常在^………$开始+结束标记.引用"模式"是可选的.
的RewriteRules
以下示例以PHP为中心,稍微增量,更容易适应类似情况.它们只是摘要,通常链接到更多变体或详细的问答.
静态映射
/contact,/about将一些页面名称缩短为内部文件方案非常简单:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^contact$ templ/contact.html RewriteRule ^about$ about.php数字标识符
/object/123引入类似于
http://example.com/article/531现有PHP脚本的快捷方式也很容易.可以将数字占位符重新映射到$_GET参数:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^article/(\d+)$ article-show.php?id=$1 # ?????????????????????????????Slug风格的占位符
/article/with-some-title-slug您可以轻松扩展该规则以允许
/article/title-string占位符:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^article/([\w-]+)$ article-show.php?title=$1 # ??????????????????????????????????请注意,您的脚本 必须能够(或适应)将这些标题映射回数据库ID.仅凭RewriteRules无法凭空创建或猜测信息.
带有数字前缀的S ..
/readable/123-plus-title因此,您经常会看到
/article/529-title-slug在实践中使用的混合路径:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^article/(\d+)-([\w-]+)$ article.php?id=$1&title=$2 # ?????????????????????????????????现在你可以跳过传递
title=$2,因为你的脚本通常依赖于数据库id.在-title-slug已经成为任意URL装饰.与替代名单的一致性
/foo/…/bar/…/baz/…如果您有多个虚拟页面路径的类似规则,则可以使用
|备用列表进行匹配和压缩.再次将它们重新分配给内部GET参数:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)# ??????????????????????????? RewriteRule ^(blog|post|user)/(\w+)$ disp.php?type=$1&id=$2 # ?????????????????????????????????????如果
RewriteRule这太复杂,你可以将它们分成单独的s.Dispatching related URLs to different backends
/date/SWITCH/backendA more practical use of alternative lists are mapping request paths to distinct scripts. For example to provide uniform URLs for an older and a newer web application based on dates:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)# ??????????????????????????????? # ? ????????????????????????????? RewriteRule ^blog/(2009|2010|2011)/([\d-]+)/?$ old/blog.php?date=$2 RewriteRule ^blog/(\d+)/([\d-]+)/?$ modern/blog/index.php?start=$2 # ????????????????????????????????????????This simply remaps 2009-2011 posts onto one script, and all other years implicitly to another handler. Note the more specific rule coming first. Each script might use different GET params.
Other delimiters than just
/path slashes
/user-123-nameYou're most commonly seeing RewriteRules to simulate a virtual directory structure. But you're not forced to be uncreative. You can as well use
-hyphens for segmenting or structure.
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^user-(\d+)$ show.php?what=user&id=$1 # ???????????????????????????????? # This could use `(\w+)` alternatively for user names instead of ids.For the also common
/wiki:section:Page_Namescheme:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^wiki:(\w+):(\w+)$ wiki.php?sect=$1&page=$2 # ???????????????????????????? ? # ??????????????????????????????Occasionally it's suitable to alternate between
/-delimiters and:or.in the same rule even. Or have two RewriteRules again to map variants onto different scripts.Optional trailing
/slash
/dir=/dir/When opting for directory-style paths, you can make it reachable with and without a final /
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^blog/([\w-]+)/?$ blog/show.php?id=$1 # ??Now this handles both
http://example.com/blog/123and/blog/123/. And the/?$approach is easy to append onto any other RewriteRule.Flexible segments for virtual paths
.*/.*/.*/.*Most rules you'll encounter map a constrained set of
/…/resource path segments to individual GET parameters. Some scripts handle a variable number of options however. The Apache regexp engine doesn't allow optionalizing an arbitrary number of them. But you can easily expand it into a rule block yourself:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)Rewriterule ^(\w+)/?$ in.php?a=$1 Rewriterule ^(\w+)/(\w+)/?$ in.php?a=$1&b=$2 Rewriterule ^(\w+)/(\w+)/(\w+)/?$ in.php?a=$1&b=$2&c=$3 # ???????????????????????????????????????????If you need up to five path segments, then copy this scheme along into five rules. You can of course use a more specific
[^/]+placeholder each. Here the ordering isn't as important, as neither overlaps. So having the most frequently used paths first is okay.Alternatively you can utilize PHPs array parameters via
?p[]=$1&p[]=$2&p[]=3query string here - if your script merely prefers them pre-split. (Though it's more common to just use a catch-all rule, and let the script itself expand the segments out of the REQUEST_URI.)See also: How do I transform my URL path segments into query string key-value pairs?
Optional segments
prefix/opt?/.*A common variation is to have optional prefixes within a rule. This usually makes sense if you have static strings or more constrained placeholders around:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^(\w+)(?:/([^/]+))?/(\w+)$ ?main=$1&opt=$2&suffix=$3Now the more complex pattern
(?:/([^/])+)?there simply wraps a non-capturing(?:…)group, and makes it optional)?. The contained placeholder([^/]+)would be substitution pattern$2, but be empty if there's no middle/…/path.Capture the remainder
/prefix/123-capture/…/*/…whatever…As said before, you don't often want too generic rewrite patterns. It does however make sense to combine static and specific comparisons with a
.*sometimes.
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^(specific)/prefix/(\d+)(/.*)?$ speci.php?id=$2&otherparams=$2This optionalized any
/…/…/…trailing path segments. Which then of course requires the handling script to split them up, and variabl-ify extracted parameters itself (which is what Web-"MVC" frameworks do).Trailing file "extensions"
/old/path.HTMLURLs don't really have file extensions. Which is what this entire reference is about (= URLs are virtual locators, not necessarily a direct filesystem image). However if you had a 1:1 file mapping before, you can craft simpler rules:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^styles/([\w\.\-]+)\.css$ sass-cache.php?old_fn_base=$1 RewriteRule ^images/([\w\.\-]+)\.gif$ png-converter.php?load_from=$2Other common uses are remapping obsolete
.htmlpaths to newer.phphandlers, or just aliasing directory names only for individual (actual/real) files.Ping-Pong (redirects and rewrites in unison)
/ugly.html??/prettySo at some point you're rewriting your HTML pages to carry only pretty links, as outlined by deceze. Meanwhile you'll still receive requests for the old paths, sometimes even from bookmarks. As workaround, you can ping-pong browsers to display/establish the new URLs.
This common trick involves sending a 30x/Location redirect whenever an incoming URL follows the obsolete/ugly naming scheme. Browsers will then rerequest the new/pretty URL, which afterwards is rewritten (just internally) to the original or new location.
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)# redirect browser for old/ugly incoming paths RewriteRule ^old/teams\.html$ /teams [R=301,QSA,END] # internally remap already-pretty incoming request RewriteRule ^teams$ teams.php [QSA,END]Note how this example just uses
[END]instead of[L]to safely alternate. For older Apache 2.2 versions you can use other workarounds, besides also remapping query string parameters for example: Redirect ugly to pretty URL, remap back to the ugly path, without infinite loopsSpaces ? in patterns
/this+that+It's not that pretty in browser address bars, but you can use spaces in URLs. For rewrite patterns use backslash-escaped
\?spaces. Else just"-quote the whole pattern or substitution:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule "^this [\w ]+/(.*)$" "index.php?id=$1" [L]Clients serialize URLs with
+or%20for spaces. Yet in RewriteRules they're interpreted with literal characters for all relative path segments.
Frequent duplicates:
Catch-all for a central dispatcher/front-controller script
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !-f RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !-d RewriteRule ^.*$ index.php [L]Which is often used by PHP frameworks or WebCMS/portal scripts. The actual path splitting then is handled in PHP using
$_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"]. So conceptionally it's pretty much the opposite of URL handling "per mod_rewrite". (Just useFallBackResourceinstead.)Remove
www.from hostnameNote that this doesn't copy a query string along, etc.
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)# ???????????? RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www\.(.+)$ [NC] ? RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://%1/$1 [R=301,L] ? # ? ?????????????????? # ?????????????????See also:
· URL rewriting for different protocols in .htaccess
· Generic htaccess redirect www to non-www
· .htaccess - how to force "www." in a generic way?Note that RewriteCond/RewriteRule combos can be more complex, with matches (
%1and$1) interacting in both directions even: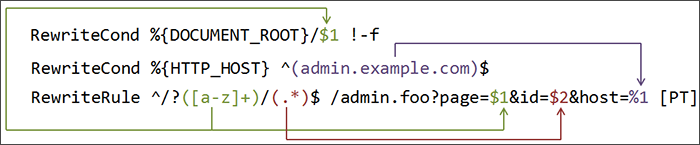
Apache manual - mod_rewrite intro, Copyright 2015 The Apache Software Foundation, AL-2.0Redirect to
HTTPS://
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteCond %{SERVER_PORT} 80 RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://example.com/$1 [R,L]"Removing" the PHP extension
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME}.php -f RewriteRule ^(.+)$ $1.php [L] # or [END]Aliasing old .html paths to .php scripts
See: http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/rewrite/remapping.html#backward-compatibility
Rewrite from URL like "/page" to a script such as "/index.php/page"
Redirect subdomain to a folder
Prevalent .htaccess pitfalls
Now take this with a grain of salt. Not every advise can be generalized to all contexts. This is just a simple summary of well-known and a few unobvious stumbling blocks:
Enable
mod_rewriteand.htaccessTo actually use RewriteRules in per-directory configuration files you must:
Check that your server has
AllowOverride Allenabled. Otherwise your per-directory.htaccessdirectives will go ignored, and RewriteRules won't work.Obviously have
mod_rewriteenabled in yourhttpd.confmodules section.Prepend each list of rules with
RewriteEngine Onstill. While mod_rewrite is implicitly active in<VirtualHost>and<Directory>sections, the per-directory.htaccessfiles need it individually summoned.
The leading slash
^/won't matchYou shouldn't start your
.htaccessRewriteRule patterns with^/normally:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteRule ^/article/\d+$ … ?This is often seen in old tutorials. And it used to be correct for ancient Apache 1.x versions. Nowadays request paths are conveniently fully directory-relative in
.htaccessRewriteRules. Just leave the leading/out.· Note that the leading slash is still correct in
<VirtualHost>sections though. Which is why you often see it^/?optionalized for rule parity.
· Or when using aRewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI}you'd still match for a leading/.
· See also Webmaster.SE: When is the leading slash (/) needed in mod_rewrite patterns?<IfModule *>wrappers begone!You've probably seen this in many examples:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)<IfModule mod_rewrite.c> Rewrite… </IfModule>- It does make sense in
<VirtualHost>sections - if it was combined with another fallback option, such as ScriptAliasMatch. (But nobody ever does that). - And it's commonly distributed for default
.htaccessrulesets with many open source projects. There it's just meant as fallback, and keeps "ugly" URLs work as default.
However you don't want that usually in your own
.htaccessfiles.- Firstly, mod_rewrite does not randomly disengage. (If it did, you'd have bigger problems).
- Were it really be disabled, your RewriteRules still wouldn't work anyway.
- It's meant to prevent HTTP
500errors. What it usually accomplishes is gracing your users with HTTP404errors instead. (Not so much more user-friendly if you think about it.) - Practically it just suppresses the more useful log entries, or server notification mails. You'd be none the wiser as to why your RewriteRules never work.
What seems enticing as generalized safeguard, often turns out to be an obstacle in practice.
- It does make sense in
Don't use
RewriteBaseunless neededMany copy+paste examples contain a
RewriteBase /directive. Which happens to be the implicit default anyway. So you don't actually need this. It's a workaround for fancy VirtualHost rewriting schemes, and misguessed DOCUMENT_ROOT paths for some shared hosters.It makes sense to use with individual web applications in deeper subdirectories. It can shorten RewriteRule patterns in such cases. Generally it's best to prefer relative path specifiers in per-directory rule sets.
Disable
MultiViewswhen virtual paths overlapURL rewriting is primarily used for supporting virtual incoming paths. Commonly you just have one dispatcher script (
index.php) or a few individual handlers (articles.php,blog.php,wiki.php, …). The latter might clash with similar virtual RewriteRule paths.A request for
/article/123for example could map toarticle.phpwith a/123PATH_INFO implicitly. You'd either have to guard your rules then with the commonplaceRewriteCond!-f+!-d, and/or disable PATH_INFO support, or perhaps just disableOptions -MultiViews.Which is not to say you always have to. Content-Negotiation is just an automatism to virtual resources.
Ordering is important
See Everything you ever wanted to know about mod_rewrite if you haven't already. Combining multiple RewriteRules often leads to interaction. This isn't something to prevent habitually per
[L]flag, but a scheme you'll embrace once versed. You can re-re-rewrite virtual paths from one rule to another, until it reaches an actual target handler.Still you'd often want to have the most specific rules (fixed string
/forum/…patterns, or more restrictive placeholders[^/.]+) in the early rules. Generic slurp-all rules (.*) are better left to the later ones. (An exception is aRewriteCond -f/-dguard as primary block.)Stylesheets and images stop working
When you introduce virtual directory structures
/blog/article/123this impacts relative resource references in HTML (such as<img src=mouse.png>). Which can be solved by:- Only using server-absolute references
href="/old.html"orsrc="/logo.png" - Often simply by adding
<base href="/index">into your HTML<head>section. This implicitly rebinds relative references to what they were before.
You could alternatively craft further RewriteRules to rebind
.cssor.pngpaths to their original locations. But that's both unneeded, or incurs extra redirects and hampers caching.- Only using server-absolute references
RewriteConds just mask one RewriteRule
A common misinterpetation is that a RewriteCond blocks multiple RewriteRules (because they're visually arranged together):
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} localhost RewriteRule ^secret admin/tools.php RewriteRule ^hidden sqladmin.cgiWhich it doesn't per default. You can chain them using the
[S=2]flag. Else you'll have to repeat them. While sometimes you can craft an "i- 很长一段时间没有看到这样一个美丽的答案!我正在读它时,我的眼睛在发光.请不要停止发布这样的答案:) (3认同)
mod_rewrite的替代品
可以在不使用RewriteRules的情况下实现许多基本的虚拟URL方案.Apache允许在没有.php扩展名的情况下调用PHP脚本,并使用虚拟PATH_INFO参数.
使用PATH_INFO,Luke
现在
AcceptPathInfo On通常默认启用.这基本上允许.php和其他资源URL携带虚拟参数:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)http://example.com/script.php/virtual/path现在,这将
/virtual/path显示在PHP中$_SERVER["PATH_INFO"],您可以根据需要处理任何额外的参数.这不是作为具有Apache的单独的输入路径段成为方便
$1,$2,$3和将它们作为不同$_GET变量来PHP.它只是用较少的配置工作来模拟"漂亮的URL".启用MultiViews以隐藏
.php扩展名.php在URL中避开"文件扩展名" 的最简单选项是:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)Options +MultiViews由于匹配的基本名称,这为Apache
article.php请求启用了Apache选择/article.这与上述PATH_INFO功能一起使用效果很好.所以你可以使用像这样的URLhttp://example.com/article/virtual/title.如果您有一个带有多个PHP调用点/脚本的传统Web应用程序,这是有意义的.请注意,MultiViews具有不同/更广泛的用途.它会导致非常小的性能损失,因为Apache总是查找具有匹配基本名称的其他文件.它实际上意味着内容协商,这样浏览器就接收可用资源中的最佳替代品(如
article.en.php,article.fr.php,article.jp.mp4).用于无扩展
.php脚本的SetType或SetHandler避免
.php在URL中携带后缀的更直接的方法是为其他文件方案配置PHP处理程序.最简单的选项是通过.htaccess以下方式覆盖默认的MIME /处理程序类型:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)DefaultType application/x-httpd-php这样您就可以将
article.php脚本重命名为article(不带扩展名),但仍将其作为PHP脚本处理.现在这可能会带来一些安全性和性能影响,因为所有无扩展文件现在都将通过PHP传输.因此,您也可以仅为单个文件设置此行为:
Run Code Online (Sandbox Code Playgroud)<Files article> SetHandler application/x-httpd-php # or SetType </Files>这在某种程度上取决于您的服务器设置和使用的PHP SAPI.常见的替代品包括
ForceType application/x-httpd-php或AddHandler php5-script.再次注意,此类设置从一个
.htaccess文件夹传播到子文件夹.您始终应该禁用静态资源,上传/目录等的脚本执行(SetHandler None和/Options -Exec或php_flag engine off等).其他Apache重写方案
在众多选项中,Apache提供了一些
mod_alias功能 - 有时mod_rewrite与rewriteRules一样有效.请注意,大多数必须在一个<VirtualHost>部分中设置,而不是在每个目录的.htaccess配置文件中.ScriptAliasMatch主要用于CGI脚本,但也适用于PHP.它允许regexp像任何一样RewriteRule.事实上,它可能是配置全能前控制器的最强大的选择.简单地
Alias帮助一些简单的重写方案.甚至
ErrorDocument可以使用普通指令让PHP脚本处理虚拟路径.请注意,这是一个kludgy解决方法,但是,除了GET请求之外什么都禁止,并且根据定义泛滥error.log.
| 归档时间: |
|
| 查看次数: |
27836 次 |
| 最近记录: |